£38.37 Original price was: £38.37.£26.86Current price is: £26.86.
- Experience the difference quality makes.
- Made of environmentally friendly materials
- Experience the Best Quality
- Hassle-Free Payments

Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Canine Hepatic Wet Dog Food – 12 x 420G Description & Review
Royal Canin Canine Adult Hepatic Wet Dog Food Cans – 12 x 420g
Manufacturer’s View
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
A low sodium intake helps decrease portal hypertension and reduces extravascular fluid loss.
A low copper with increased zinc content aims to minimise intracellular copper accumulation and thus hepatocellular injury.
The synergistic antioxidant complex slows hepatocyte degradation and helps neutralise free radicals.
Adapted energy levels help maintain bodyweight in dogs with hepatic failure. L-carnitine favours fat metabolism in the liver avoiding excessive protein catabolism.
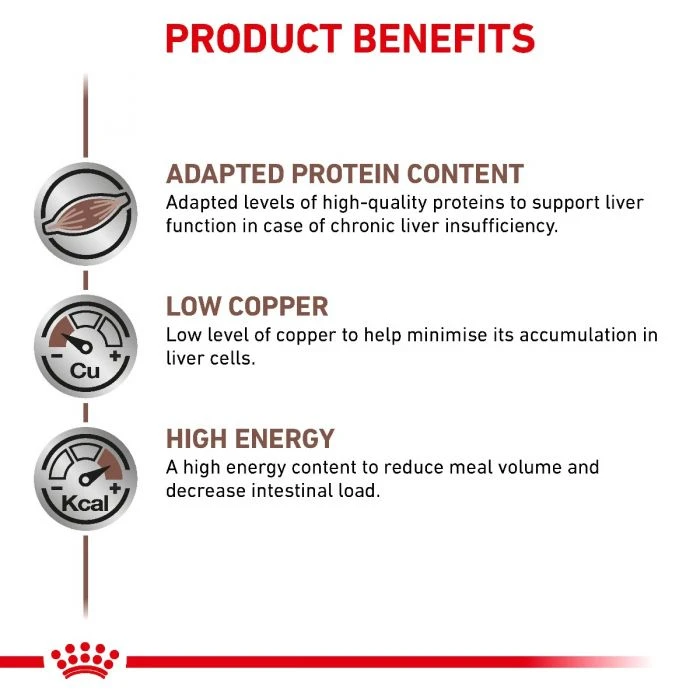
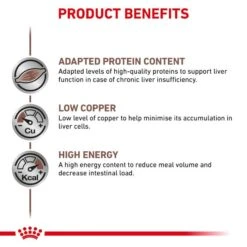
Key Benefits
Electrolyte Balance
Low Copper
Antioxidant Complex
Adapted Energy
Electrolyte Balance
Low Copper
Antioxidant Complex
Adapted Energy
Recommended for
Dogs with liver disease, chronic hepatitis, portosystemic shunt, hepatic encephalopathy, copper metabolism disorders.
Dogs with liver disease, chronic hepatitis, portosystemic shunt, hepatic encephalopathy, copper metabolism disorders.
Dogs with liver disease, chronic hepatitis, portosystemic shunt, hepatic encephalopathy, copper metabolism disorders.
_______________________________________________
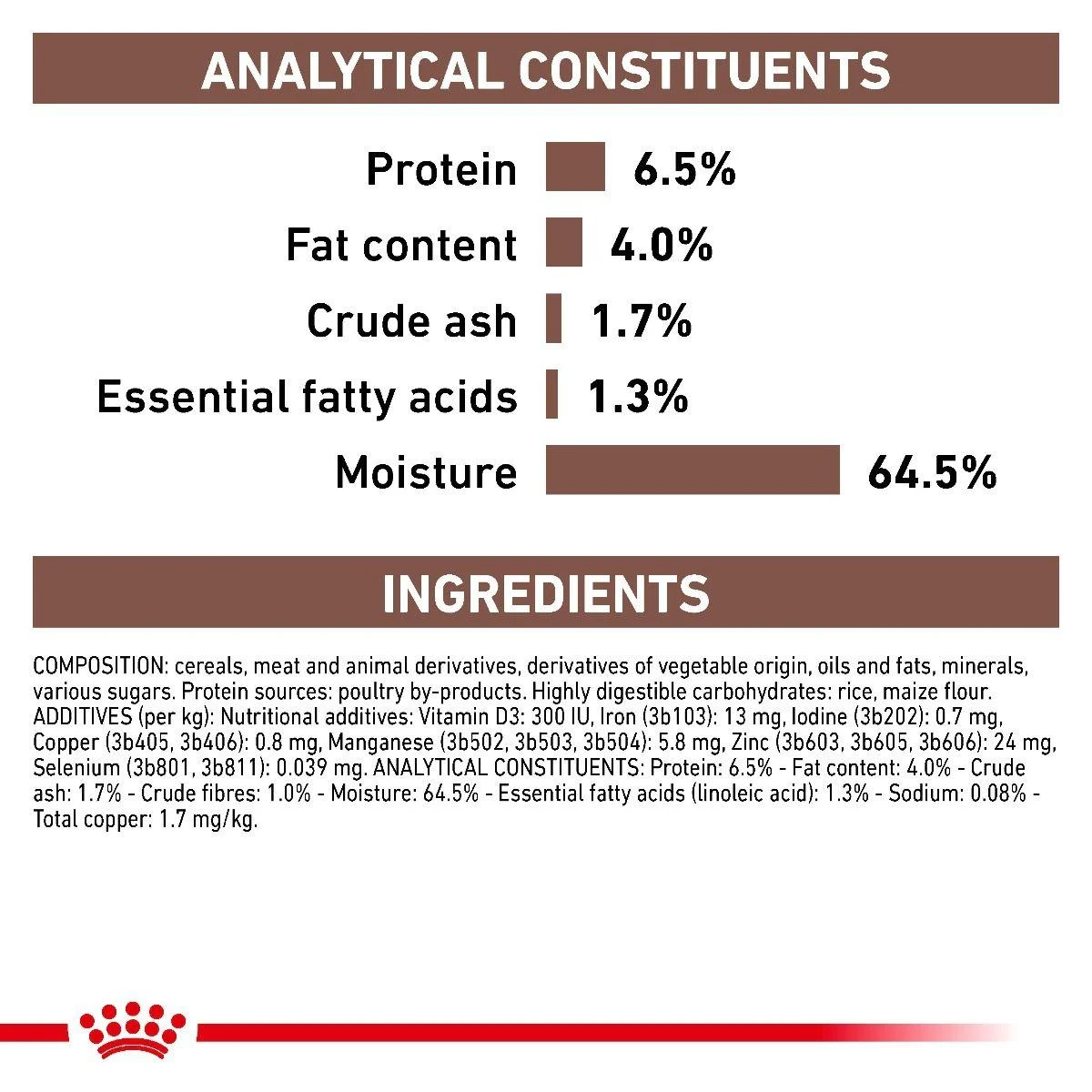
Ingredients
Rice, corn grains and flour, poultry meats and livers, sunflower oil, dried egg white, cellulose, sugar beet pulp, minerals, carrageenan, taurine, L-carnitine, Fructo-Oligo-Saccharides (FOS), trace elements (including chelated trace elements), marigold meal (rich in lutein), vitamins. Crude ash: 4.2%. Crude fibre: 5.6%. Crude oil fats: 11.7%. Moisture: 64%. Protein: 18.1%.
_________________________________________________________________________________
Nutrition and Analytical Constituents
____________________________________________________________________________________
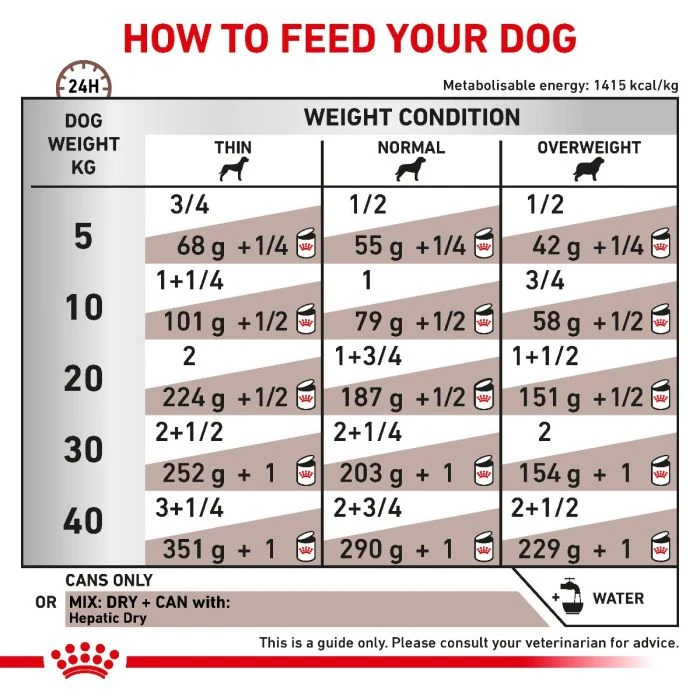
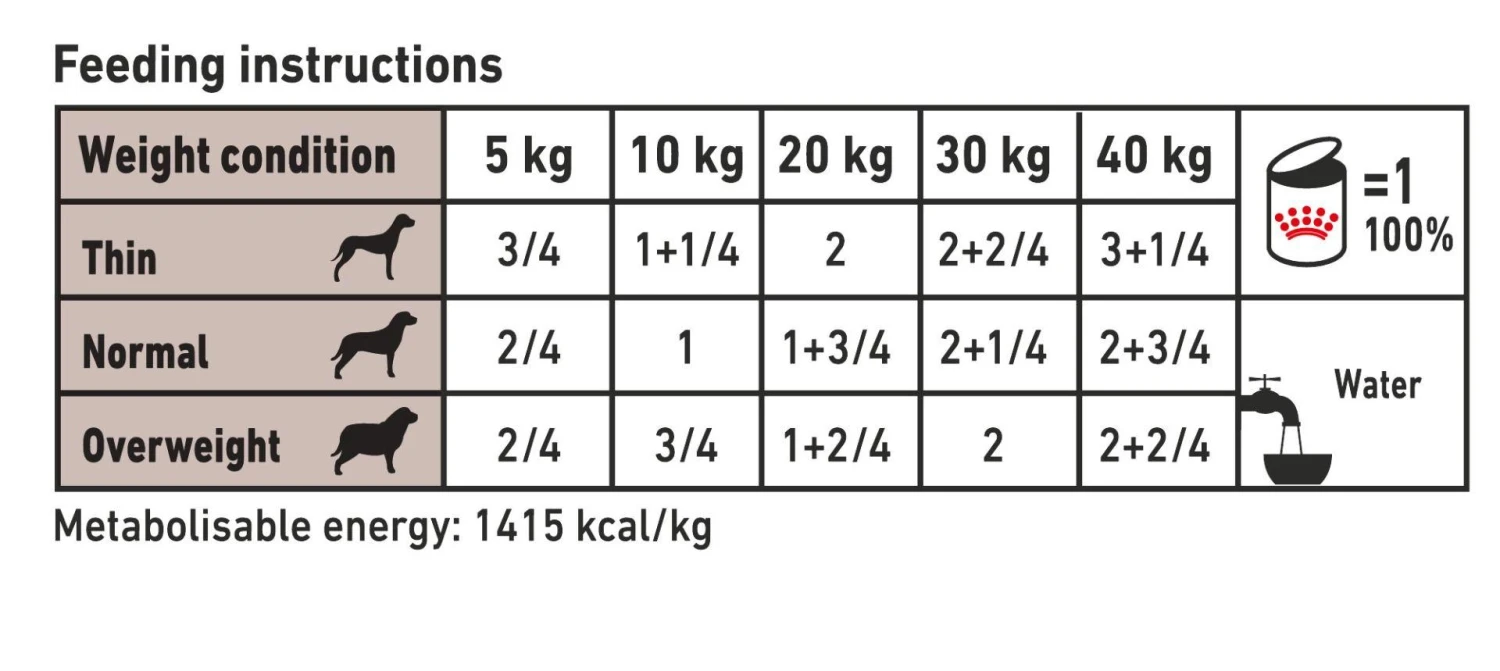
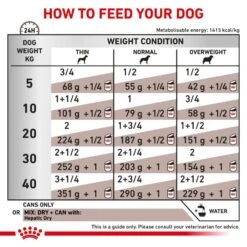
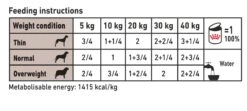
Daily Feeding Guide
For further information on this product and daily feeding guidelines please consult a veterinary surgeon.
For further information on this product and daily feeding guidelines please consult a veterinary surgeon.
For further information on this product and daily feeding guidelines please consult a veterinary surgeon.
Be the first to review “Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Canine Hepatic Wet Dog Food – 12 X 420G” Cancel reply
Related products
Dog Cans & Pouches
Hill’s Prescription Diet I/d Low Fat Digestive Care Wet Dog Food – 12x360g
Dog Cans & Pouches
Winalot Sunday Dinner In Gravy Wet Dog Food Pouches – 40 X 100g
Dog Cans & Pouches
Dog Cans & Pouches
Dog Cans & Pouches
Billy + Margot Adult Lamb & Superfoods Wet Dog Food Cans – 12 X 395g
Dog Cans & Pouches
Dog Cans & Pouches
Dog Cans & Pouches
Dechra Specific COW-HY Food Allergy Management Plus Wet Dog Food – 6 X 300G
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.